Abstract: Understand 6.4 let’s you create your own metrics.
Understand comes with a lot of built-in metrics, like the number of code lines or the McCabe cyclomatic complexity of a function. Not only can you view and export these values, but you can also use them in other Understand views. For example, you can shade the nodes in a call tree by cyclomatic complexity, find outliers with treemaps, or sort by metrics in the locator.
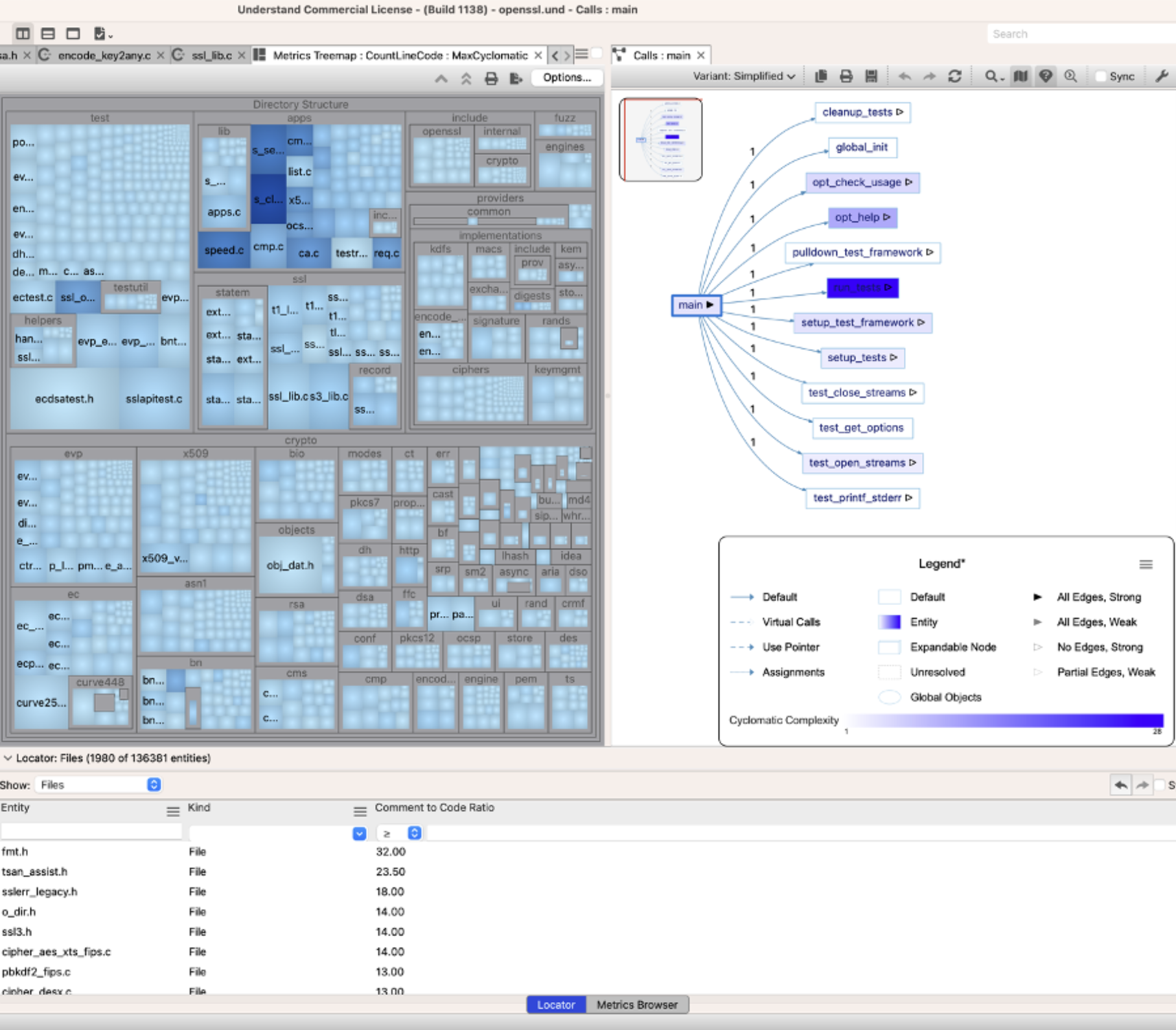
But, what if you wanted a call tree shaded by test coverage or by Git churn? Understand 6.4 allows you to add metrics plugins!
Understand Plugins
Understand plugins are Perl or Python scripts, usually ending in a .upl or .upy extension respectively. They can be used for graphs, CodeCheck checks, and interactive reports. Just drag the .upy or .upl file onto the Understand GUI and select install.
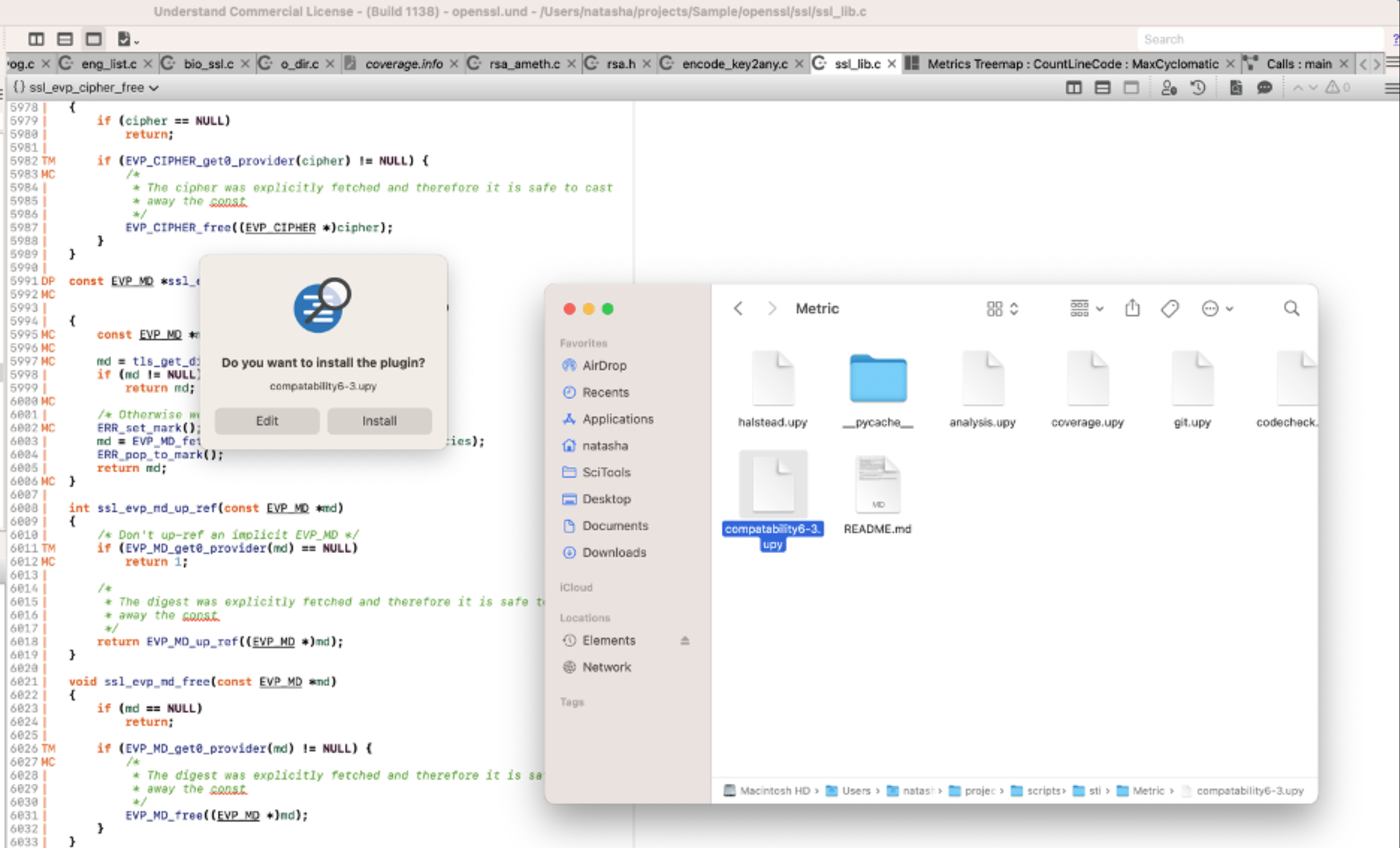
Plugins then populate menus or options in the Understand user interface:
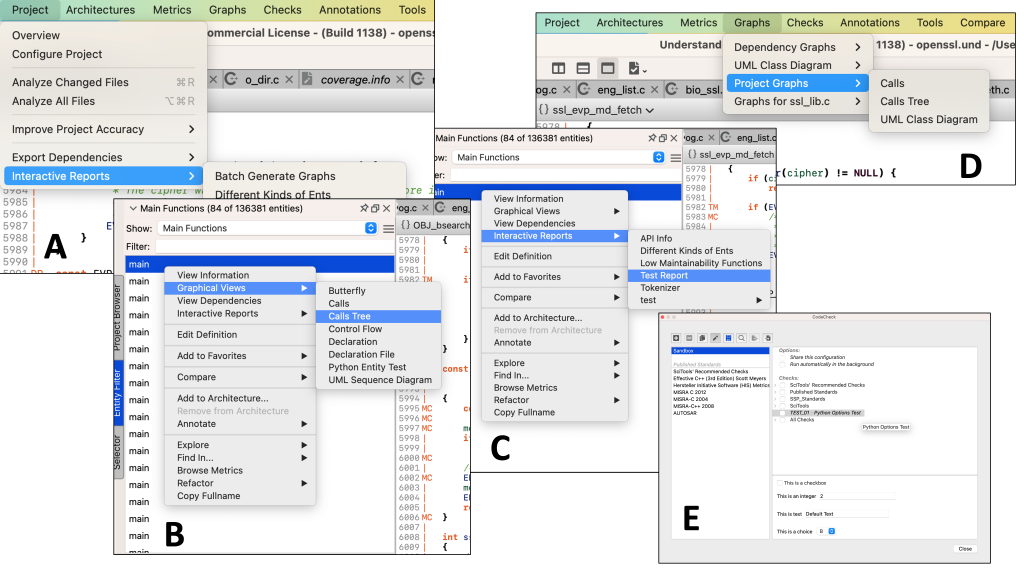
Metric Plugins
Metric plugins are Python scripts (Perl is not supported) and can be installed the same as any other Understand plugin. Once installed, the metrics will appear in any metric list where they’re applicable.
How to Write Your Own Metric Plugin
Check out some of the existing metric plugins at our plugin repository. The compatability6-3 plugin is the template plugin described in the Python API documentation. It can be a great place to start.
The main function of a Metric Plugin is the “value” function which should return a number. It takes a Metric plugin object with information about the requested metric and database and a target. The target can be an entity, architecture, or database. Note that database metrics are not directly visible in the Understand GUI. Instead, most database level metrics are architecture metrics that run on the “Directory Structure” architecture. Database metrics can be accessed from the Perl and Python APIs.
The other functions in a metric plugin provide information about the metric (ID, name, description) and when it is available (test_entity, test_architecture, and so on).
What if My Metric Plugin is Really Slow?
No problem. Most places that use Metrics are run on background threads. You might see “Calculating” text or progress bars, but the user interface should not hang.